Translate this page into:
Ear sign in tinea faciei
*Corresponding author: Surya Bramara Merla, Department of Dermatology, Father Muller Medical College, Mangaluru, Karnataka, India. mshree1998@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Kiran, Bhat RM, Merla SB. Ear sign in tinea faciei. J Skin Sex Transm Dis. doi: 10.25259/JSSTD_32_2025
A 40-year-old female presented with a history of redness and flaking over the left ear and face associated with itching for a six-week duration with no similar complaints over other areas of the body or in family members. Examination revealed diffuse erythema and whitish dry scales seen over the pinna and a few lesions extending onto the mandibular area, suggestive of “ear sign of tinea faciei.” [Figure 1]. The diagnosis of tinea was confirmed by potassium hydroxide mount, which showed fungal hyphae. The patient was initiated on oral itraconazole 5 mg/kg and topical azole.
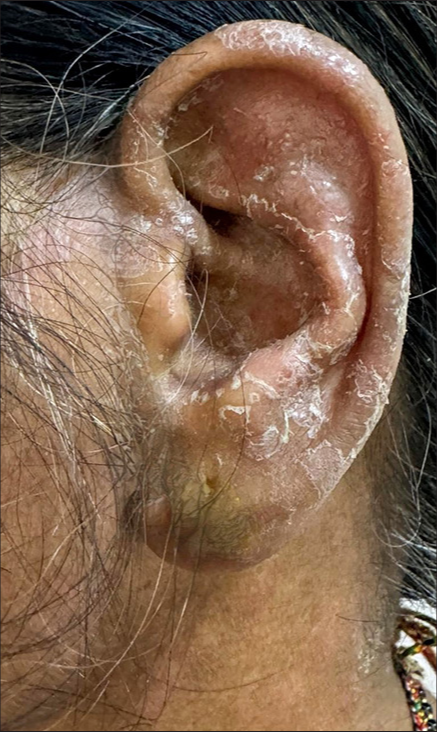
- Diffuse erythema and whitish dry scales seen over the pinna extending onto the mandibular area depicting “ear sign of tinea faciei.”
Dermatophytosis is the most common reason for dermatologic consultations in India. However, they have recently posed diagnostic challenges for various reasons, one of the common being the use of over-the-counter topical steroid-combined antifungals, thereby modifying the morphology of lesions. Tinea faciei, unlike the other forms of tinea, need not always present with the classical annular erythematous plaques with superficial scales but can present with just erythema, scaling, and papules. Hence, diagnosis of tinea faciei requires expertise. To make things easier, “ear sign of tinea faciei” was coined wherein erythema and scaling over the auricular pinna suggest a diagnosis of tinea faciei. Earlier, “ear sign of tinea capitis” was mentioned wherein lesions over the helix, antihelix, and retroauricular region, sparing the retroauricular fold, characterize tinea capitis, helping it differentiate it from seborrheic dermatitis.
Dermatologists must diligently look for these signs to make an accurate diagnosis, helping to prevent unnecessary tests and incorrect treatments.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Financial support and sponsorship: Nil.






