Translate this page into:
Herpes zoster maxillaris: Clinical, dermoscopic, and microscopic features
*Corresponding author: Vishal Gaurav, Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, India. mevishalgaurav@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Danish M, Chandra A, Bhagwat A, Gaurav V. Herpes zoster maxillaris: Clinical, dermoscopic, and microscopic features. J Skin Sex Transm Dis. 2024;6:215-6 doi: 10.25259/JSSTD_19_2024
A 25-year-old male presented with a painful vesicular eruption on the right side of his face associated with painful erosions in the oral cavity for two days. The mother recalled him having varicella in his childhood years. He did not have any systemic illness or prior similar episodes. Physical examination revealed eroded vesicles on an erythematous base over the right infraorbital area, right nasofacial sulcus, including the tip of the nose, right infranasal area, and right side of the upper lip [Figure 1a]. Examination of oral cavity showed erosions and grouped vesiculopustules on an erythematous base involving the right side of the palate [Figure 1b]. Examination of eye, nasal cavity and ear were unremarkable, except for mild right lower eyelid edema. Dermoscopy showed brownish crusts with polyglobular structures and background erythema [Figure 2]. Tzanck smear showed many multinucleated giant cells [Figure 3]. The diagnosis of right-sided trigeminal herpes zoster maxillaris was made. He was prescribed oral acyclovir (800 mg 5 times a day) for a week along with diclofenac 50 mg twice daily for pain relief, resulting in complete resolution of the lesions as well as associated symptoms [Figures 4a and b].
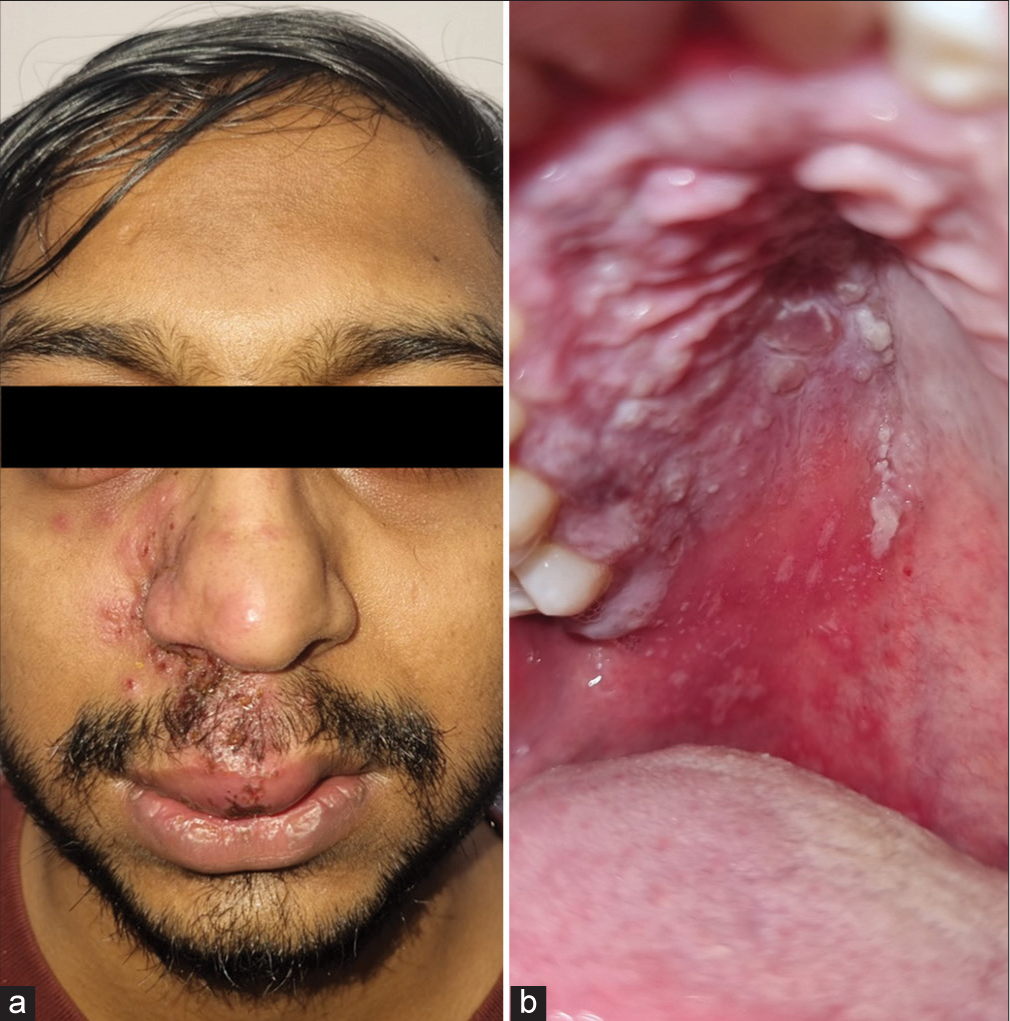
- (a): Eroded vesicles on an erythematous base over the right infraorbital area, right nasofacial sulcus, including the tip of the nose, right infranasal area, and right side of the upper lip and (b): Oral cavity showing erosions and grouped vesiculopustules on an erythematous base involving the right half of the palate.
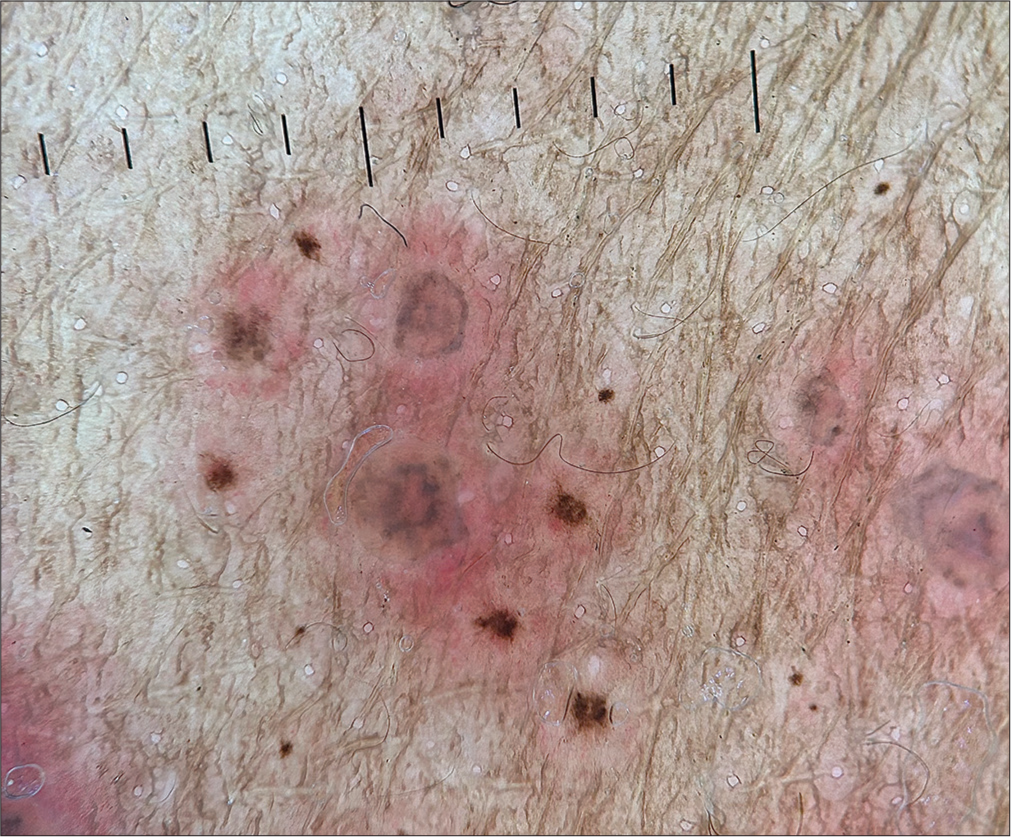
- Dermoscopy (Illuco, IDS-1100) showing brownish crusts with polyglobular structures and background erythema (Polarized, ×20).
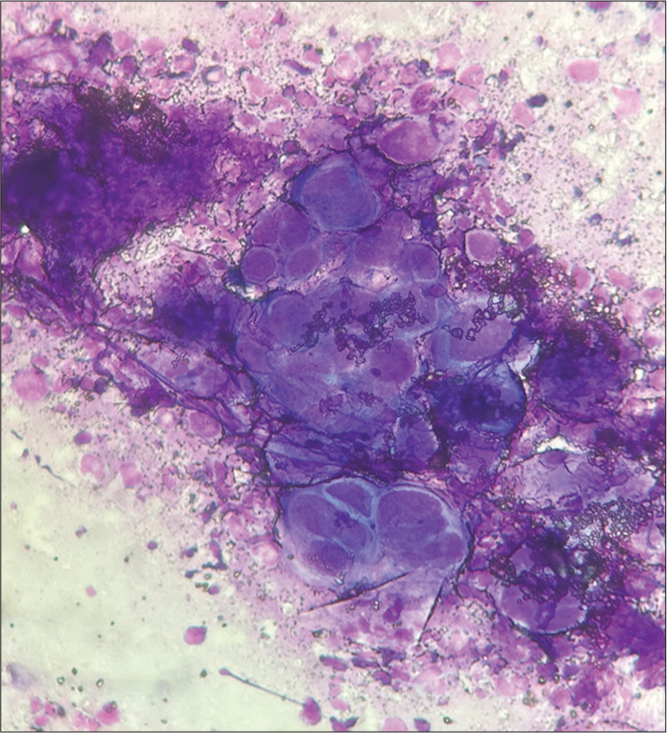
- Tzanck smear showing multinucleated giant cells (Giemsa stain ×1000).
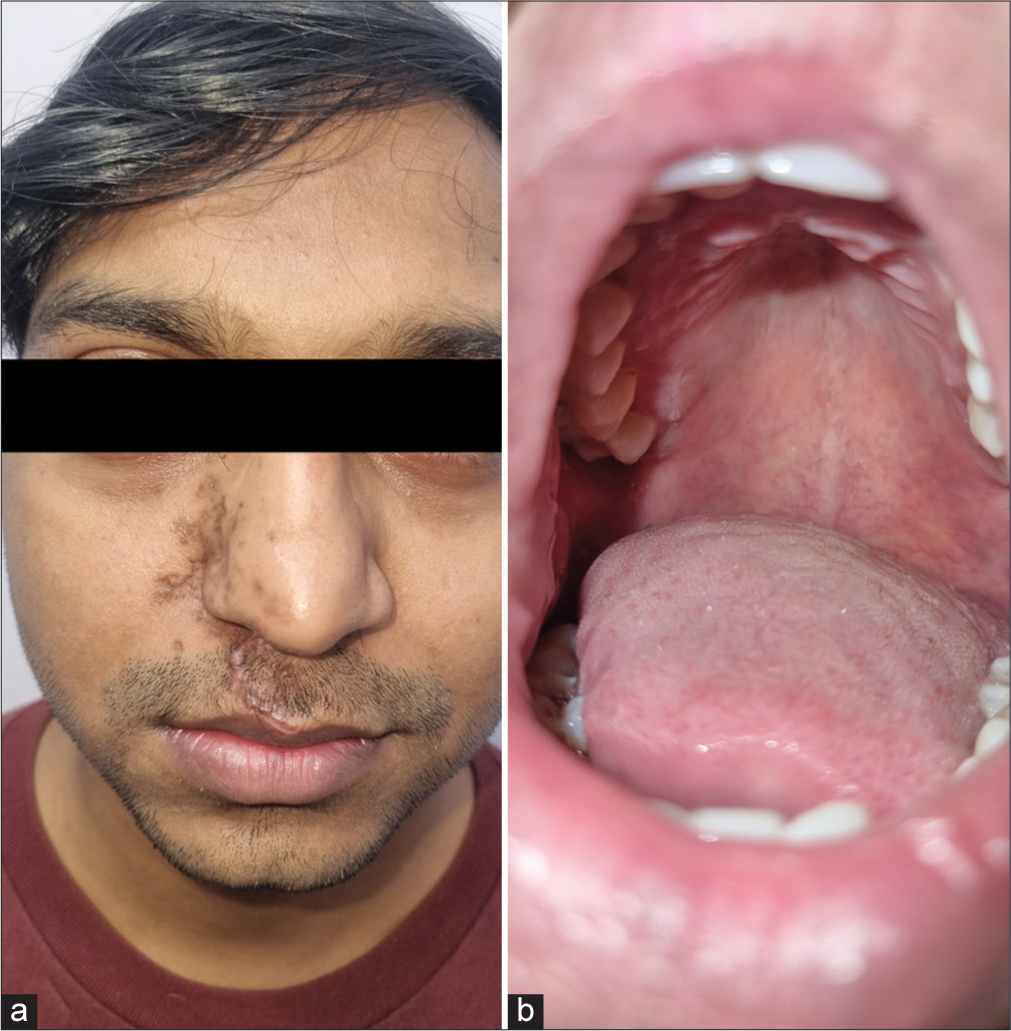
- Resolution of (a): Cutaneous and (b): oral lesions following treatment.
Ethical approval
The Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.





