Translate this page into:
Quiz questions from dermoscopy of inflammatory dermatoses (inflammoscopy)
*Corresponding author: Vishal Gaurav, Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Pt. Madan Mohan Malaviya Hospital, New Delhi, India. mevishalgaurav@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Kuchana P, Gaurav V, Misri R. Quiz questions from dermoscopy of inflammatory dermatoses (inflammoscopy). J Skin Sex Transm Dis. doi: 10.25259/JSSTD_91_2024
QUESTIONS
-
What pattern is observed in Kyrle disease under dermoscopy?
Three-zone concentric pattern
Two-zone concentric pattern
Central white/brown crust
Both a and b
-
What pattern is observed in lichen amyloidosis?
Two-zone pattern
Hub and spoke pattern
Both a and b
None
-
What is a distinguishing dermoscopic feature of Darier’s disease?
Dark brown polygonal/round structures surrounded by a peripheral gray-white halo
Central keratotic plug
White homogeneous area around the central plaque
Follicular plugs surrounded by white color
-
Which condition shows twisted hairs forming loops and irregular coils with perifollicular scales under dermoscopy?
Keratosis pilaris
Lichen planus
Lichen amyloidosis
Pityriasis rubra pilaris
-
What dermoscopic finding is typical for lichen nitidus?
Central brown area
White globules with sharp margins and lack of skin creases
Peripheral brown structureless area
Dotted vessels
-
Which dermatosis is associated with white or gray lines over a diffuse gray-brown structureless area on dermoscopy, typically observed on the flexural aspects of the wrists, forearms, and lower legs?
Psoriasis
Eczema
Lichen planus
Darier’s disease
-
What are common findings in psoriasis under dermoscopy?
Yellow-white structureless areas
Blue dots and lines
Peripheral pigmented reticular lines
Uniform dotted vessels
-
Which dermatosis is characterized by follicular plugs and a perifollicular yellow halo?
Keratosis pilaris
Pityriasis rubra pilaris
Lichen spinulosus
Lichen planopilaris
-
Which condition exhibits a cerebriform surface formed by sulci and gyri on dermoscopy?
Exogenous ochronosis
Squamous cell carcinoma
Seborrheic melanosis
Gougerot–Carteaud syndrome
-
Which dermatosis displays central red dots and globules with peripheral radiating white lines on dermoscopy?
Lichen amyloidosis
Lichen planus hypertrophicus
Prurigo nodularis
Lichen simplex chronicus
-
What is a common dermoscopic feature of pityriasis rosea?
Brown dots over an ill-defined white area
Pigmented reticular lines
Central white globules
Peripheral white scaling collarette with a jagged inner free edge
-
Which dermatosis presents with diffuse brown structureless areas with ostial sparing on dermoscopy?
Melasma
Gougerot–Carteaud syndrome
Macular amyloidosis
Facial acanthosis nigricans
-
What dermoscopic pattern is seen in follicular eczema?
Central white/brown crust
Follicular plugs surrounded by white color
Central brown star-like areas
Yellow-white septa delimiting holes
-
Which dermatosis presents with a brown peripheral keratotic tract with a double free edge on dermoscopy?
Pityriasis rubra pilaris
Darier’s disease
Gougerot–Carteaud syndrome
Porokeratosis
-
What dermoscopic features are seen in dermatitis neglecta?
Polygonal plate-like brown scales arranged in a mosaic-like pattern
Peripheral small cornflake-like scales
Background erythema
All the above
-
Which condition shows yellowish-white septa delimiting holes with dotted vessels inside under dermoscopy?
Darier’s disease
Lichen planus
Lichen simplex chronicus
Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf
-
Which condition features yellowish-white lacunar areas with scattered specks of necrosis on dermoscopy?
Perniosis
Langerhans cell histiocytosis
Sweat dermatitis
Lichen nitidus
-
What dermoscopic finding is characteristic of macular amyloidosis?
Alternating parallel hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation
White structureless areas with peripheral white projections
Follicular orange-yellow areas
Central white globules
-
Which condition features irregular brown-gray globular, annular, and arciform structures and blue-gray amorphous areas obliterating follicular openings on dermoscopy?
Exogenous ochronosis
Lichen planus pigmentosus
Frictional melanosis
Melasma
-
Which condition features linear crista cutis and sulcus cutis under dermoscopy?
Facial acanthosis nigricans
Idiopathic eruptive macular pigmentation
Seborrheic keratosis
Both a and b
-
Which dermoscopic pattern of Wickham striae is shown in Figure 1?
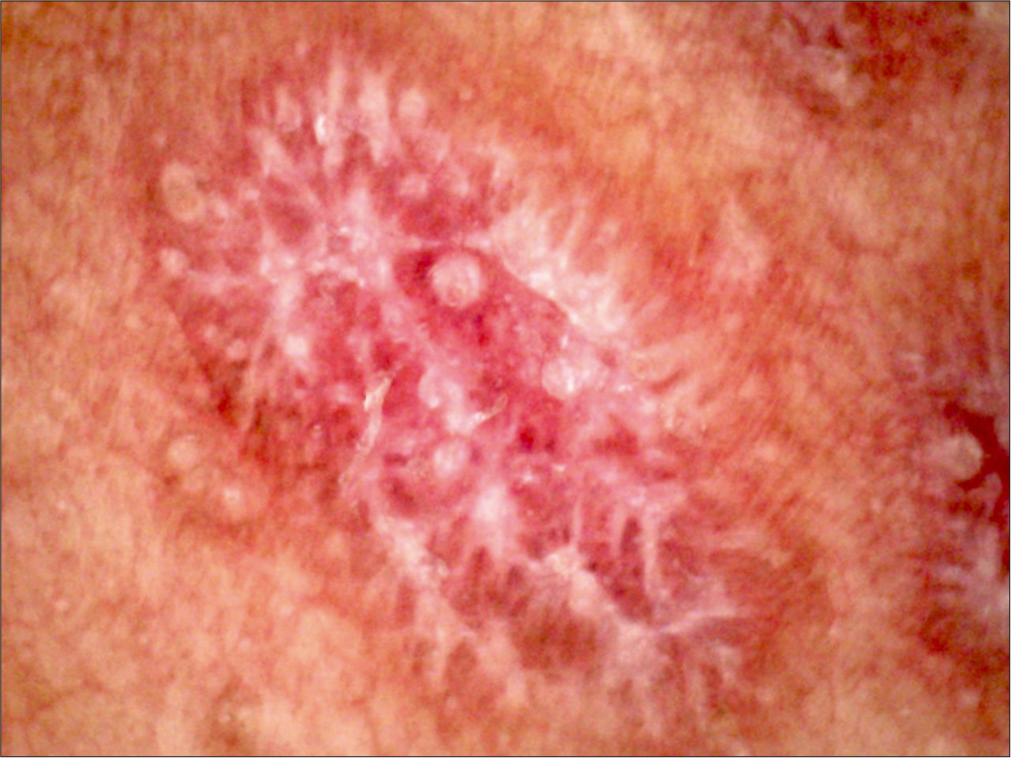 Figure 1:
Figure 1:- Dermoscopy (AM7115MZT Dino-Lite Edge 3.0 digital microscope) of lesions on the right hand (polarized; ×35).
-
A young female presented with patchy hair loss over the scalp for 3 months. The trichoscopic image is shown in Figure 2. What is your diagnosis, and what does the red arrows indicate?
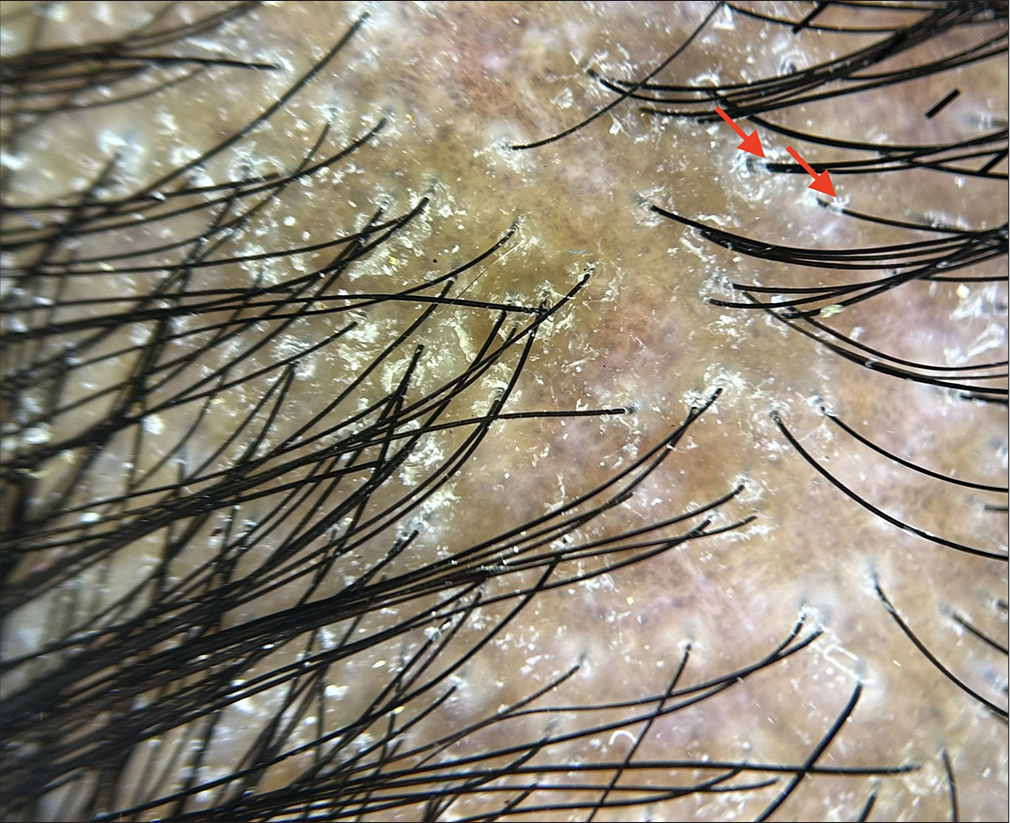 Figure 2:
Figure 2:- Dermoscopy (HeineDELTA one) of scalp (polarized; ×10) showing marked structures (red arrows).
-
A 38-year-old female patient presented with multiple papules with central crusting, some mildly pruritic and others asymptomatic, over the bilateral thighs. Name the pattern and sign (indicated by the black arrow) shown in the dermoscopy in Figure 3.
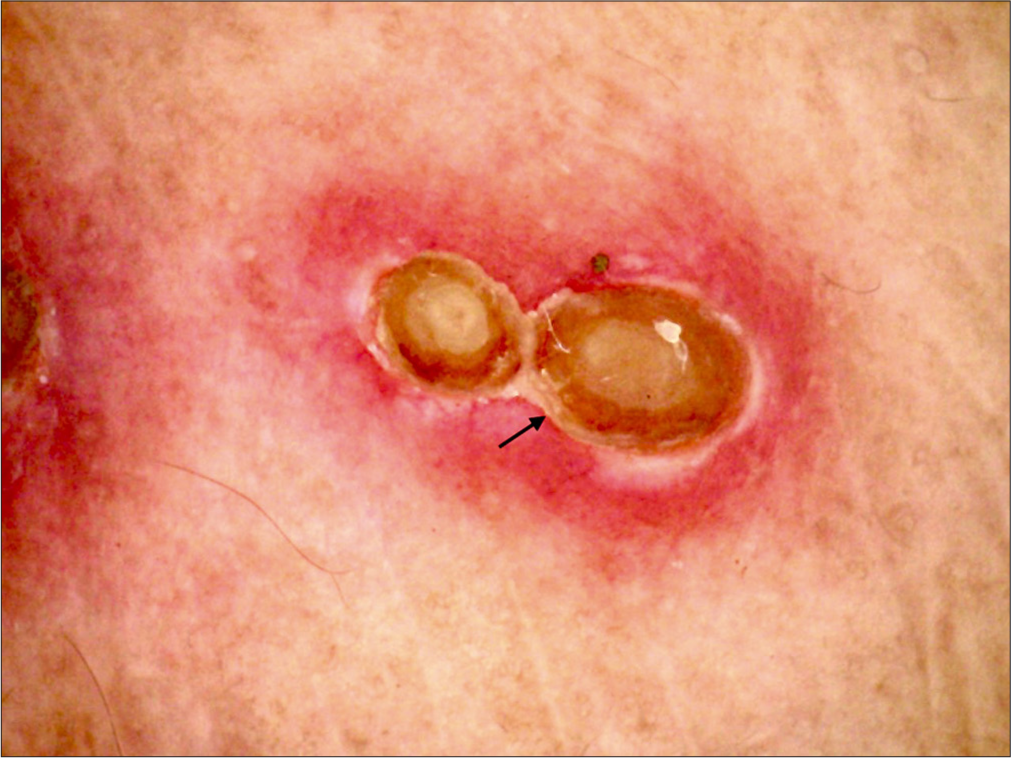 Figure 3:
Figure 3:- Dermoscopy (AM7115MZT Dino-Lite Edge 3.0 digital microscope) of lesions on the right thigh (polarized; ×20) showing marked structure (black arrow).
-
A middle-aged female presented with diffuse slate-gray pigmentation over her face and neck for 1 year. The dermoscopic image is shown in Figure 4. What is your diagnosis?
 Figure 4:
Figure 4:- Dermoscopy (HeineDELTA one) of face (polarized; ×10).
-
A 14-year-old male patient presented with multiple erythematous to hyperpigmented papules over the bilateral arms for 6 months. Figure 5 shows the dermoscopic image. What is the diagnosis?
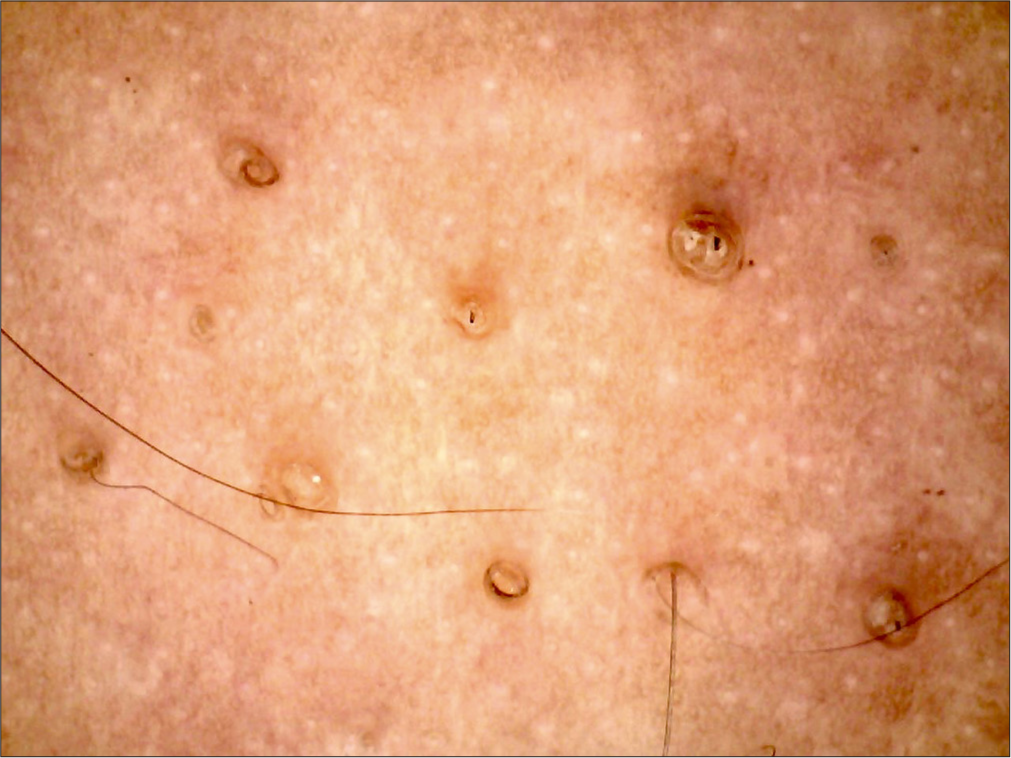 Figure 5:
Figure 5:- Dermoscopy (AM7115MZT Dino-Lite Edge 3.0 digital microscope) of lesions on the arm (polarized; ×35).
-
A middle-aged female presented with patchy hair loss on the scalp and pigmented plaques behind the bilateral ears extending into the scalp for 6 months. The dermoscopic image is shown in Figure 6. What is the diagnosis?
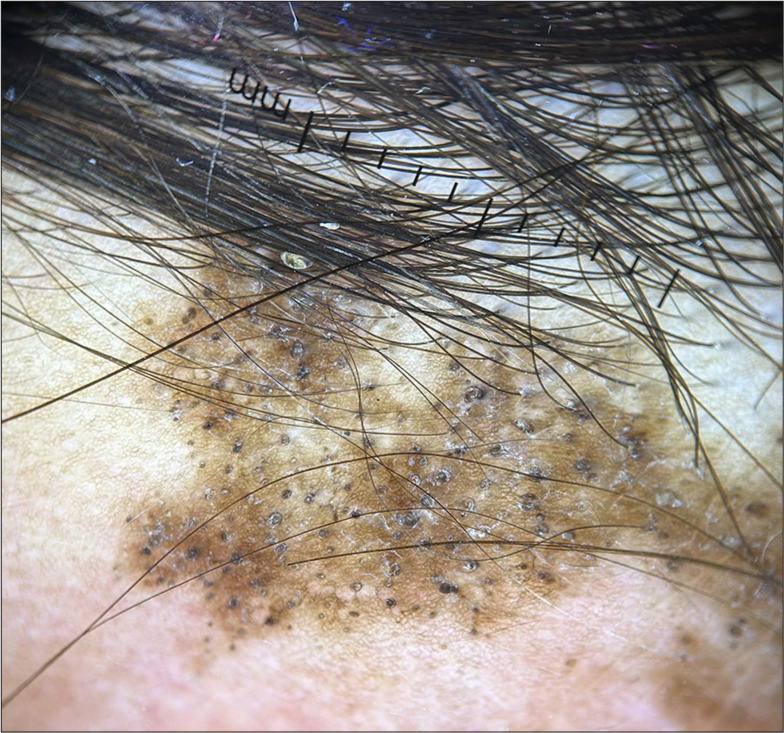 Figure 6:
Figure 6:- Dermoscopy (HeineDELTA one) of scalp (polarized; ×10).
-
A 44-year-old female patient presented with hyperpigmentation over the bilateral cheeks for 3 years, with accentuation noted on sun exposure. The patient has a history of applying topical medications for the same. The dermoscopic image is shown in Figure 7. What is the diagnosis?
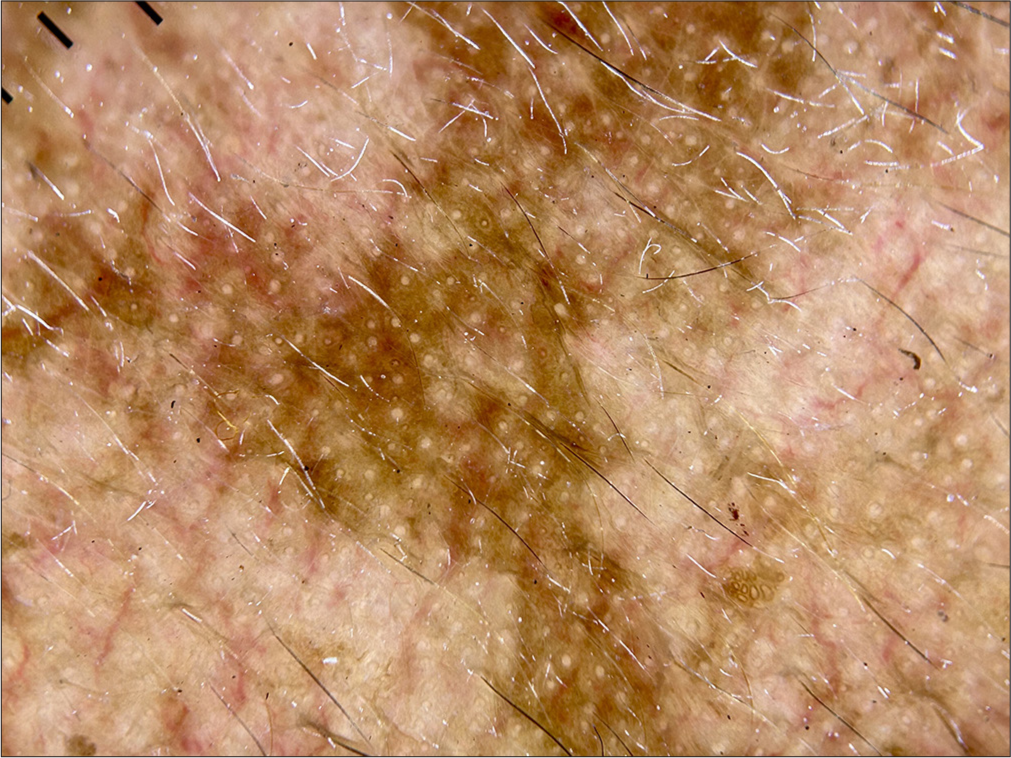 Figure 7:
Figure 7:- Dermoscopy (HeineDELTA one) of right cheek (polarized; ×10).
-
A 25-year-old female presented with intensely pruritic papules over the extremities for 6 months. The dermoscopic image of the papule is shown in Figure 8. What is the diagnosis?
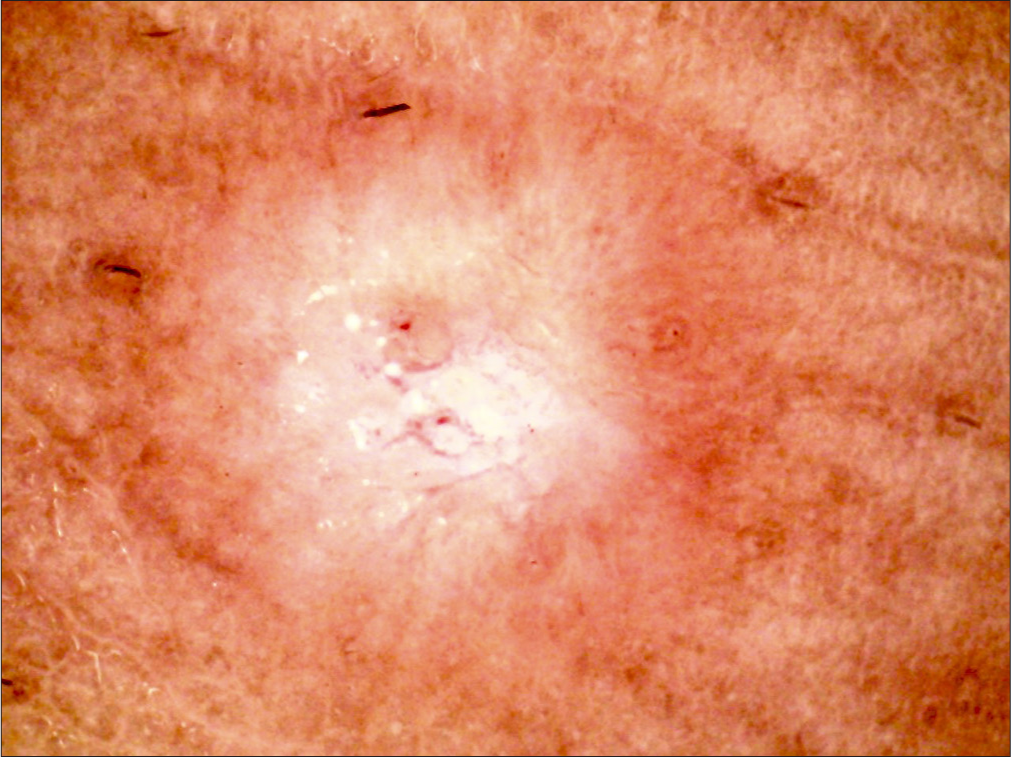 Figure 8:
Figure 8:- Dermoscopy (AM7115MZT Dino-Lite Edge 3.0 digital microscope) of lesions on the right leg (polarized; ×35).
-
A 28-year-old male presented with a hypopigmented atrophic plaque over the right side of the neck for 6 months [Figure 9a]. The dermoscopic image is shown in Figure 9b. What is the diagnosis?
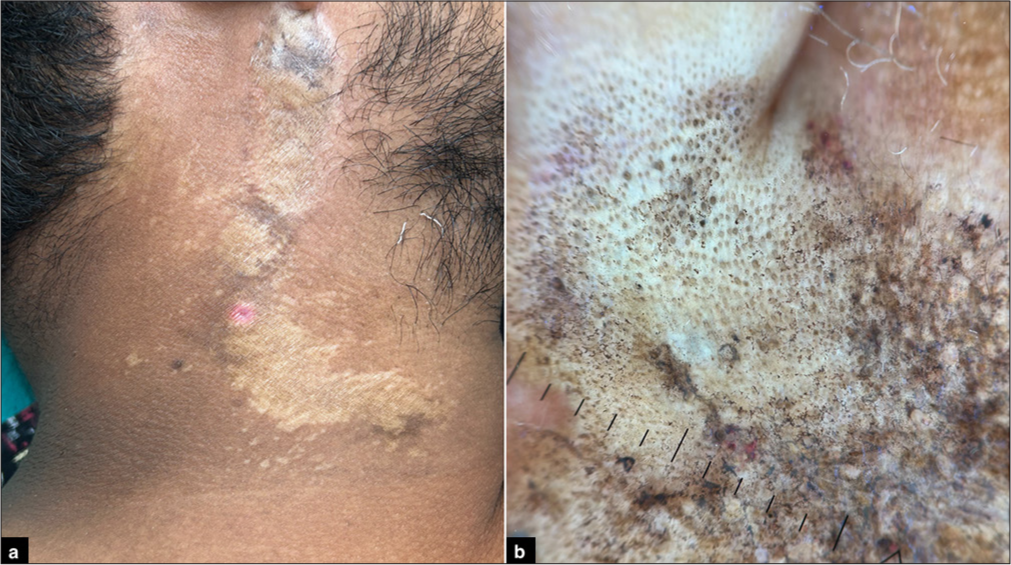 Figure 9:
Figure 9:- Images showing (a): Atrophic plaque on right side of the neck; (b): Dermoscopy (HeineDELTA one) of the atrophic plaque (polarized; ×10).
-
A 22-year-old female presented with widespread erythema with discrete to coalescing pustules associated with severe pruritus. The dermoscopic image is shown in Figure 10. What is the diagnosis?
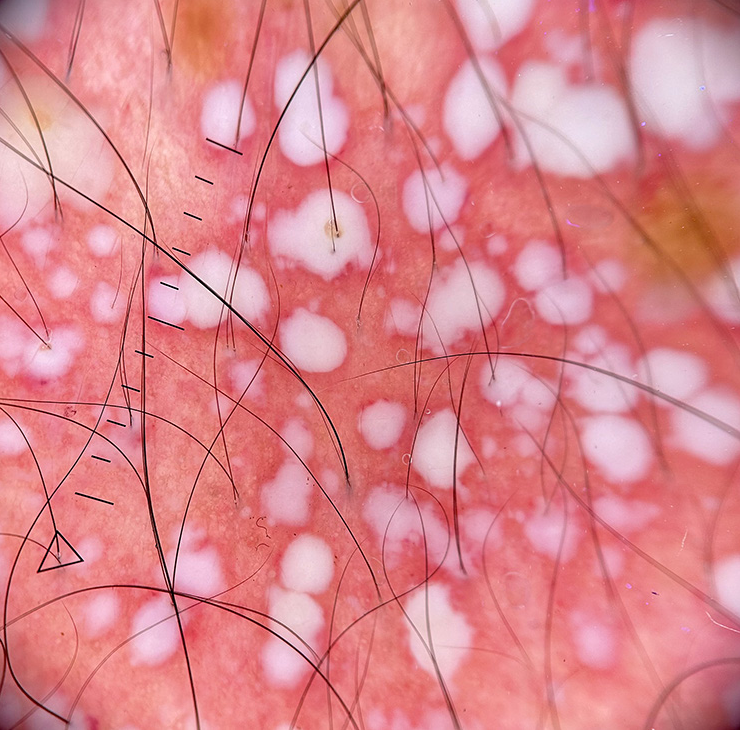 Figure 10:
Figure 10:- Dermoscopy (HeineDELTA one) of lesions on the abdomen (polarized; ×10).
ANSWERS
(d). Kyrle disease, also known as hyperkeratosis follicularis et parafollicularis in cutem penetrans, is a variant of primary perforating dermatoses characterized by transepidermal elimination of endogenous material. Dermoscopy reveals a three-zonal concentric pattern characterized by bright whitish-brownish scales in the center, a structureless whitish-gray area surrounding the central crusts, and a peripheral, brown, delicate pigmentation. Two-zone patterns may also be observed.[1-4]
(c). “Two-zone pattern” (a central structureless white area of variable shade with a peripheral ridge and groove area and/or structureless pigmented area) and “hub and spoke pattern” are observed in lichen amyloidosis.[5]
(a). Darier’s disease is an autosomal dominant disorder of keratinization due to mutations in the ATP2A2 gene. The distinguishing dermoscopic features of Darier’s disease are brown polygonal or round structures (corresponding to hyperkeratosis) and the surrounding whitish halo (corresponding to acanthosis). Other findings include central light-brown follicular openings, brown lines (exaggerated pseudo-network), and white scales.[8]
(a). Dermoscopy of keratosis pilaris is characterized by the presence of vellus hairs that are frequently coiled, semi-circular, or looped; peri-follicular erythema; and peri-pilar casts. Hairs emerging in groups of two or three and vascular ectasias are also observed.[9,10]
(b). Dermoscopy of lichen nitidus is characterized by white globules with sharp margins and a lack of skin creases, typically followed by radial ridges and central circular depression. The radial ridges radiate from the edges of the central depression, giving a “sunburst appearance.”[14,15]
(c). The term Wickham striae was coined by Louis Frédéric Wickham in 1895 and corresponds to fine white or gray lines or dots seen on the top lesions of lichen planus. Dermoscopically, Wickham striae appear over a diffuse gray-brown structureless area.[7,16]
(d). The main dermoscopic feature of psoriasis is the presence of dotted vessels with unspecific or uniform distribution, along with white scales in a patchy or diffuse arrangement. Other relevant findings include pigmented structures such as brown, gray, or blue structureless areas, dots, or globules.[17-20]
(b). Dermoscopy of pityriasis rubra pilaris is characterized by whitish keratotic follicular plugs and perifollicular yellow halos, along with multiple linearly arranged and dotted vessels in an irregular pattern.[21]
(d). The “sulci and gyri” pattern (depressions and elevations presumably due to papillomatosis) and cobblestone pattern are observed in confluent and reticulated papillomatosis (Gougerot–Carteaud syndrome).[23]
(c). The most common dermoscopic findings in prurigo nodularis are peripheral radiating white lines/striations and pearly white areas with a white starburst pattern.[24]
(d). The typical dermoscopic pattern of pityriasis rosea is peripheral white scales with a jagged inner free edge.[20]
(a). The most common dermoscopic pattern seen in melasma is an accentuated pseudopigment network (diffuse brown structureless areas with ostial sparing), followed by brown dots/globules and telangiectasia.[25,26]
(b). The dermoscopy of follicular eczema presents a repetitive pattern consisting of follicular plugs with a perifollicular white color.[19,28]
(d). Dermoscopy of porokeratotic lesions reveals brown dots, globules, or lines, as well as a brown/white peripheral keratotic tract with a double free edge.[28]
(d). Dermoscopy of dermatitis neglecta shows polygonal plate-like brown scales arranged in a mosaic-like pattern, with smaller cornflake-like scales mainly on the peripheral parts of affected areas and a background of erythema.[29]
(d). Dermoscopy of acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf reveals whitish cerebriform lesions along with a network pattern composed of yellowish-white septa delimiting holes with dotted vessels inside.[30]
(c). Dermoscopy of sweat dermatitis shows yellowish-white lacunar areas with scattered necrotic specs giving a “starry sky appearance,” increased cutaneous markings, and deep brown pigmentary changes with superimposed brownish scales.[31]
(a). A rippled pigmentation on dermoscopy, seen as alternating parallel hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation, is characteristic of macular amyloidosis.[32]
(a). Dermoscopic features of exogenous ochronosis include a “diffuse brown background with blue-gray amorphous areas obliterating some follicular openings, irregular brown-gray globular, annular, and arciform structures, and worm-like patterns.”[36]
(a). Dermoscopy of facial acanthosis nigricans reveals linear crista cutis, sulcus cutis, and hyperpigmented dots in crista cutis.[40]
Leaf venation pattern. The dermoscopic pattern seen in Figure 1 is a leaf venation pattern. It is characterized by “delicate secondary striae branching from the centered Wickham’s striae venation, linked together at either end, mimicking the crystal structure of snow.” Other patterns include reticular, circular, radial streaming, linear, starburst, and globular patterns.[6,7]
Lichen planopilaris, tubular casts indicative of active disease. Trichoscopy in Figure 2 shows a patch of hair loss with perifollicular scaling, tubular cast, pigment dots, and globules. Patchy white scaling over a hyperpigmented to erythematous background is indicative of lichen planopilaris, with tubular casts (black arrows) suggesting active disease.[11-13]
Acquired perforating dermatoses, white-collar sign. Figure 3 shows the dermoscopy of acquired perforating dermatoses. A three-zone concentric pattern with a central keratotic plug, a middle white homogeneous area, and a peripheral erythematous zone is observed. The white homogeneous area surrounding the central keratotic plug is called the “white-collar sign.”[3]
Lichen planus pigmentosus. Dermoscopy in Figure 4 shows pigment dots and globules arranged in a reticulate pattern with sparing of follicular openings, as seen in lichen planus pigmentosus.[22]
Keratosis pilaris. The dermoscopy image in Figure 5 shows vellus hairs that are coiled, looped, and peripilar casts suggestive of keratosis pilaris.[9,10]
Discoid lupus erythematosus. The dermoscopy in Figure 6 shows follicular plugging, white scales, and white structureless areas on a background of brown hyperpigmentation, suggestive of discoid lupus erythematosus.[27]
Melasma. Dermoscopy in Figure 7 reveals an accentuated pseudopigment network, brown dots/ globules, and telangiectasia suggestive of melasma. Telangiectasia in the surrounding skin is due to topical steroid application.[25,26]
Prurigo nodularis. Dermoscopy in Figure 8 shows red dots and globules, pearly white areas, and a white starburst pattern with peripheral striations suggestive of prurigo nodularis.[24]
Lichen sclerosus atrophicus. Dermoscopy in Figure 9 shows white structureless areas, peppering of pigment, comedone-like openings, erythematous areas, keratotic plugs, and irregularly arranged linear vessels, suggestive of lichen sclerosus atrophicus.[33-35]
Pustular psoriasis. Dermoscopy in Figure 10 shows non-follicular milky globules on an erythematous background with a few dotted vessels. In pustular psoriasis, regularly distributed dotted vessels are seen, whereas in acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, vascular structures are absent.[37-39]
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent is not required as there are no patients in this study.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Financial support and sponsorship: Nil.
References
- Dermoscopic pattern of Kyrle's disease. An Bras Dermatol. 2020;95:244-6.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopy of Kyrle disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:e99-101.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopic features of acquired perforating dermatosis: A retrospective analysis of 19 cases. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2021;46:184-7.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans (flegel disease): Clinical, dermoscopic, and histopathologic features. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2025;16:323-5.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopic features of primary cutaneous amyloidosis in skin of colour: A retrospective analysis of 48 patients from South India. Australas J Dermatol. 2021;62:370-4.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- A study of dermoscopic patterns of Wickham's Striae in lichen planus. Int J Res Dermatol. 2022;8:206.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Zosteriform lichen planus: An uncommon presentation of a common condition. CosmoDerma. 2024;4:68.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopy of localized Darier's disease in Fitzpatrick type IV skin. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2020;11:298-300.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopy of keratosis pilaris. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2019;10:613-4.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruritic trichostasis spinulosa: A rare variant. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2024;15:487-91.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichen planopilaris: A review of evaluation methods. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2021;87:442-5.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Invisible lichen planopilaris unmasked by dermatoscopy. Int J Trichology. 2017;9:76.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopy of lichen planopilaris. J Cutan Med Surg 2024 Available from: 10.1177/12034754241308261 [Last accessed 2025 Mar 1]
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopy in general dermatology (nonneoplastic dermatoses) of skin of colour: A comparative retrospective study by the International Dermoscopy Society. Eur J Dermatol. 2020;30:688-98.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermatoscopic features of lichen nitidus. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:866-7.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis-Frédéric Wickham and the Wickham's striae of lichen planus. Skinmed. 2004;3:287-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- A cross-sectional analysis of dermoscopic patterns distinguishing between psoriasis and lichen planus: A study of 80 patients. J Evol Med Dent Sci. 2015;4:17017.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Role of dermoscopy in differentiating seborrheic dermatitis of scalp and scalp psoriasis. CosmoDerma. 2024;4:80.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Follicular psoriasis: A case report and review of literature. Skin Appendage Disord. 2024;10:148-55.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopic features of psoriasis, lichen planus, and pityriasis rosea in patients with skin type IV and darker attending the Regional Dermatology Training Centre in Northern Tanzania. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2019;9:44-51.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopy of erythrodermic pityriasis rubra pilaris. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2019;10:500-1.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopy of lichen planus pigmentosus and histopathological correlation: A case series. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2024;14:e2024254.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermatoscopy of confluent and reticulated papillomatosis (Gougerot-Carteaud syndrome) J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2017;15:836-8.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Role of dermoscopy in the diagnosis of hypertrophic lichen planus and prurigo nodularis. Indian J Dermatol. 2019;64:341.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- A clinico-epidemiological study of different dermoscopic patterns in hyperpigmented facial lesions in a tertiary care centre. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2024;17:112-23.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Implications of dermoscopy and histopathological correlation in discoid lupus erythematosus in skin of color. Indian J Dermatol. 2022;67:5.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopy of inflammatory dermatoses (inflammoscopy) in skin of color-A systematic review by the International Dermoscopy Society. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2023;13:e2023297.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopy of dermatitis neglecta in the periocular area in skin of color. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2019;11:678-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf: Dermoscopy approach in dark skin patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36:e944-5.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atypical presentation of sweat dermatitis with review of literature. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2019;10:698-703.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopy in cutaneous amyloidosis: A prospective study from India. Indian J Dermatol. 2022;67:94.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopic evaluation of extragenital lichen sclerosus et atrophicus. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2022;12:e2022125.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comedones in dermatology. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2024;90:396-407.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folliculocentric atrophic papules in a 12-year-old boy. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42:404-6.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopic criteria for differentiating exogenous ochronosis from melasma. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79:819.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Non-follicular milky globulesDermoscopy saves the day. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2017;7:35-6.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acute localised exanthematous pustulosis: A rare cause of localised sterile pustules. Indian J Dermatol. 2022;67:428-31.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- "Hypopyon" sign in dermatology. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2024;90:128-32.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinico-investigative study of facial acanthosis nigricans. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2022;13:221.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






