Translate this page into:
Snake plant-like morphology of a cutaneous horn: An unusual presentation
*Corresponding author: Chandana Shajil, Department of Dermatology, Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India. chandanashajil@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Abraham HA, Shajil C. Snake plant-like morphology of a cutaneous horn: An unusual presentation. J Skin Sex Transm Dis. doi: 10.25259/JSSTD_8_2025
A 47-year-old female presented with a 10-year history of a yellowish raised lesion over her upper lip, allegedly developing after self-manipulation of a mole-like lesion. Radiofrequency ablation was done 5 years ago, but the lesion recurred a few months later. She was otherwise healthy, with no known comorbidities. On examination, multiple clustered, curved, yellowish hard projections were seen arising from a firm base over the right side of her upper lip, surrounded by a collarette of skin [Figure 1]. The lesion’s age and clinical characteristics, including a narrow base with a significantly greater height, surface ridges, and the absence of significant tenderness and erythema, were suggestive of cutaneous horn overlying a benign lesion. Histopathological examination of the excised lesion revealed features of cutaneous horn, along with acanthosis, hypergranulosis with coarse keratohyaline granules, and vacuolated superficial keratinocytes, suggestive of verruca vulgaris [Figure 2]. There were no signs of recurrence at 1-year follow-up.
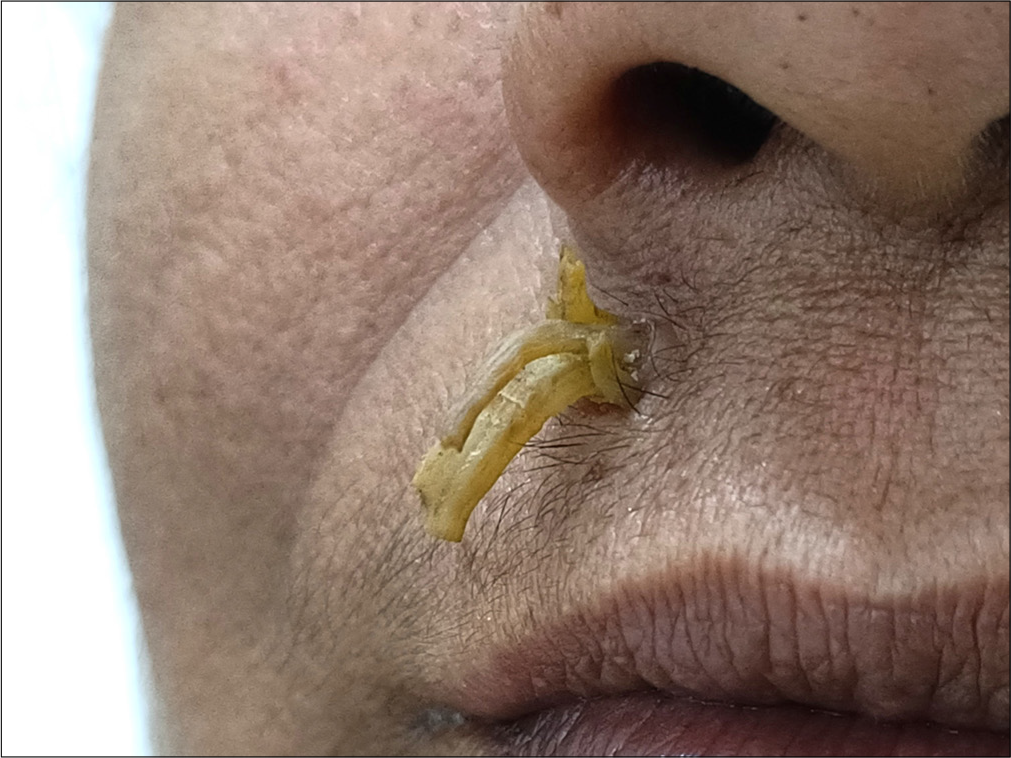
- Multiple closely clustered, curved, yellowish hard projections of different lengths, arising from of base surrounded by a collarette of skin, over the upper lip.
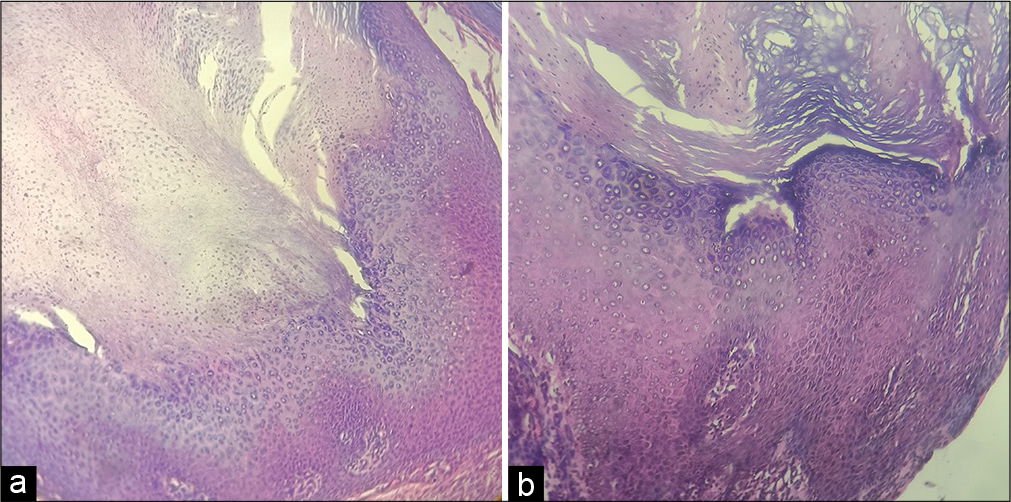
- Massive compact hyperkeratosis with orthokeratosis and parakeratosis, acanthosis, hypergranulosis with coarse keratohyaline granules, and vacuolated superficial keratinocytes (a): hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) ×10; (b): H&E ×40.
A cutaneous horn or cornu cutaneum is a hyperkeratotic, exophytic projection arising from the stratum corneum layer of the skin, with its height exceeding half the width of the base. It is the product of a reactive process driven by certain intrinsic and extrinsic factors occurring in certain benign, premalignant, or malignant skin lesions. The abnormal keratinization results in the formation of a densely compacted keratinous structure resembling an animal horn. It is typically seen over sun-exposed sites such as the face, scalp, neck, dorsum of hands, and forearms, with sizes ranging from a few millimeters to several centimeters. Histopathological examination reveals pronounced hyperkeratosis, with orthokeratosis and parakeratosis. Although the diagnosis is primarily clinical, a biopsy of the base is essential to identify the underlying skin lesion. Therefore, complete surgical excision followed by appropriate management of the underlying lesion remains the treatment of choice.
Ethical approval
The Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Financial support and sponsorship: Nil.





