Translate this page into:
A rare example of locus minoris resistentiae
*Corresponding author: Arun Somasundaram, Department of Dermatology, Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Puducherry, India. arunsomasundaram25@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Somasundaram A, Kololichalil A. A rare example of locus minoris resistentiae. J Skin Sex Transm Dis 2024;6:109-10. doi: 10.25259/JSSTD_52_2023.
A 15-year-old female consulted our outpatient department for an asymptomatic single orange-brown raised lesion over her scalp since birth. Her mother noticed a new growth with finger-like projections over the existing skin lesion for six months. On examination, there was a solitary well-defined hairless orange-brown plaque with filiform growth present over the scalp [Figure 1a]. Dermoscopic findings over the orange-brown plaque include yellowish globules on a papillary grayish-yellow background suggestive of nevus sebaceous. Dermoscopy over the filiform projections revealed hairpin vessels and thrombosed vessels suggestive of the filiform wart [Figure 1b]. Skin biopsy from the filiform projections confirmed the diagnosis of the filiform wart. Biopsy from the underlying orange-brown plaque showed orthokeratosis, acanthosis, and defective hair follicle with accumulation of sebaceous glands suggestive of nevus sebaceous. Hence, a diagnosis of filiform wart overlying a nevus sebaceous was made.
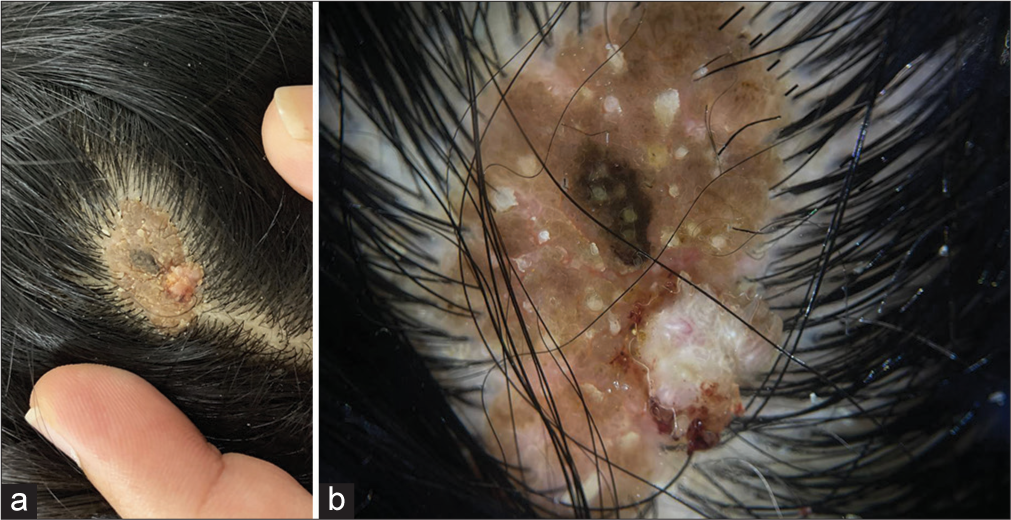
- (a): A solitary well-defined verrucous hairless orange-brown plaque with filiform growth over the vertex of the scalp; (b): Dermoscopy (Dermlite, ×10) yellowish globules on a papillary grayish-yellow background with thrombosed vessels and hairpin vessels suggestive of filiform wart overlying nevus sebaceous.
Locus minoris resistentiae (LMR) is a site that offers increased vulnerability to the onset of the disease than the rest of the body. Trauma, irradiation, chronic lymph stasis, and herpes scars act as a nidus for various other infectious, inflammatory, and neoplastic conditions. Cutaneous mosaicism serves as a congenital LMR. Others include epidermal nevus, congenital hemangioma, and linear porokeratosis, which can act as a congenital LMR.[1] This case is highlighted as an infectious lesion over an area of cutaneous mosaicism, a rare example of LMR.
Ethical approval
The Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
References
- Occurrence of filiform wart over nevus sebaceous: A report of two cases of locus minoris resistentiae. Indian J Paediatr Dermatol. 2019;20:345-7.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]





